-
PLANE WAVEFORMS
The extension of the Sine Wave in more dimensions than one is forming what is called the "Plane Waveform". Wave packets in two and three dimensions appear when "Plane Waveforms" moving in di erent directions, Superimpose.Dissipation and Disturbance of the Waveform occurs as a result of its impact with an object. These components of the Waveform from its front knocking on the object spread out, change form, or destroyed. The generated Dissipative Structure that occurs is followed by the interaction of the various components of the di erentiated Waveform.Before we can proceed with any further analysis of concepts we must clarify the meaning of a "Vector". A Vector constitutes basically a mathematical concept expressing "Size" and "Direction". Graphically we represent a Vector as an Arrow. As a writing character, this Arrow is represented by a Bold Character of the Alphabet with a small Arrow drawn over it. A Vector can be represented either by its Cartesian Coordinates, which are the projections of the Vector onto the Cartesian Axes, or its "Magnitude" and "Direction". The Direction of a Vector in 2D is generally acceptable to be represented by the Anticlockwise Angle the Vector forms with the Horizontal Axis of the Cartesian Coordinates.
This ".pdf" File Requires "Chrome 9" or higher, "Firefox 3.6" or higher, "InternetExplorer 9" or higher and the "Adobe PDF Reader" Add-on Installed to Display Properly.
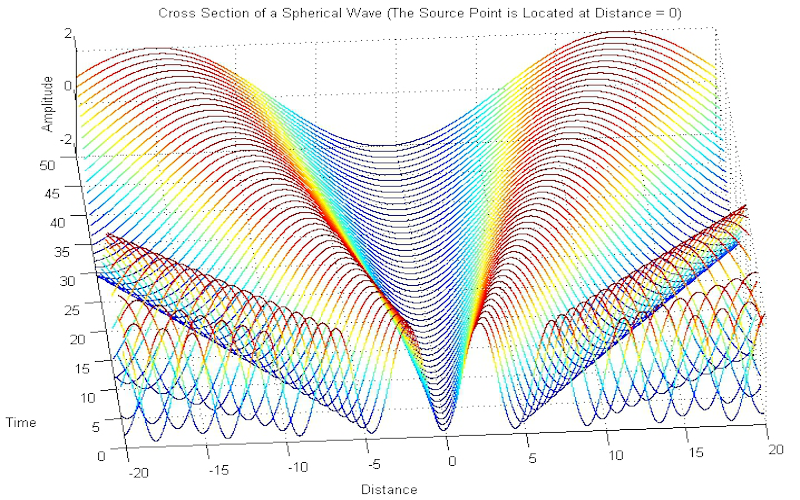
Download "SphericalWave"
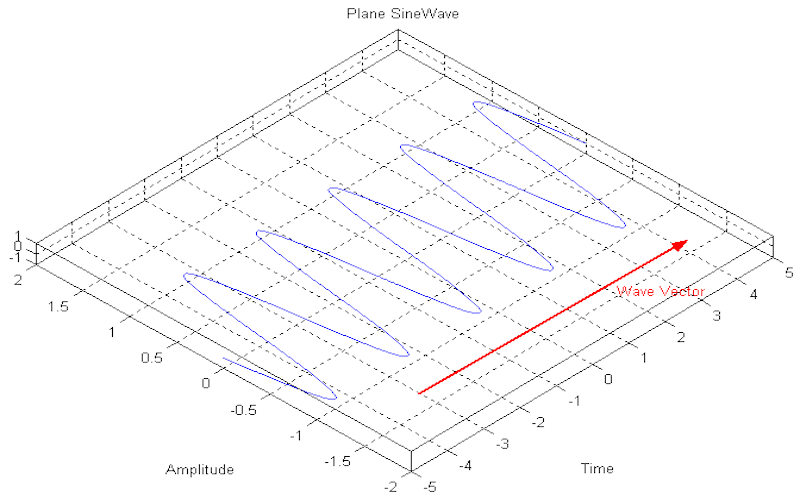
Download "PlaneSineWave(.m)"
Download "PlaneSineWave(.fig)"
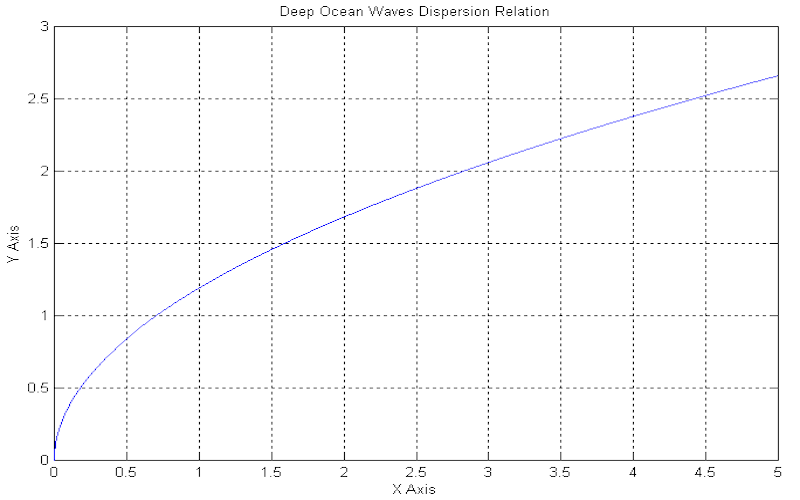
Download "OceanWavesDispersionRelation"
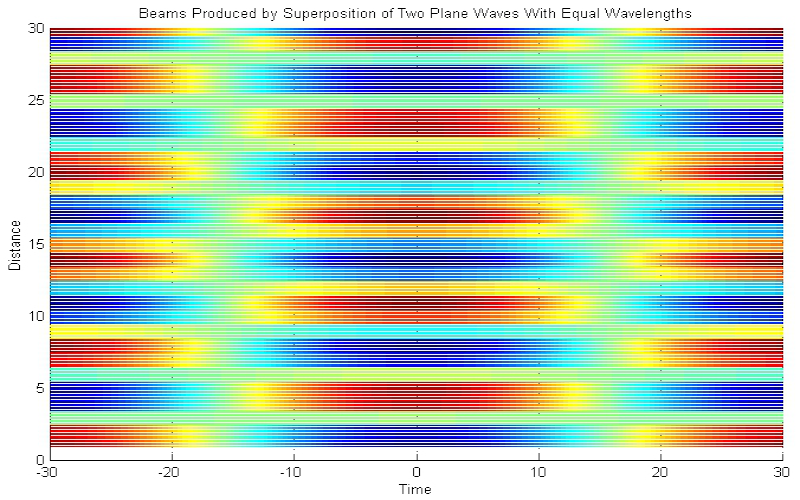
Download "BeamsEqualWavelenghts"
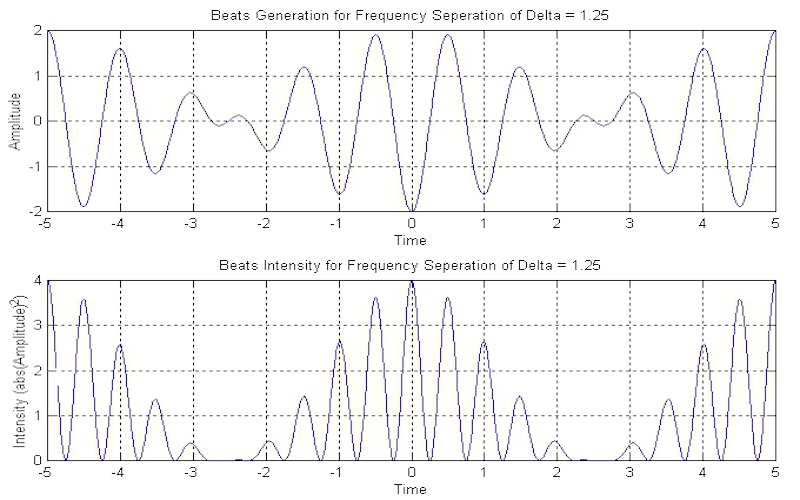
Download "BeamsGeneration1D"
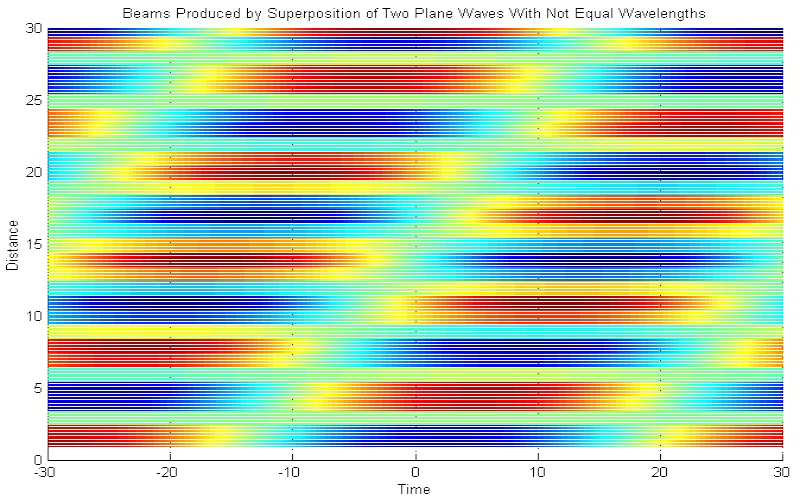
Download "BeamsNotEqualWavelengths"
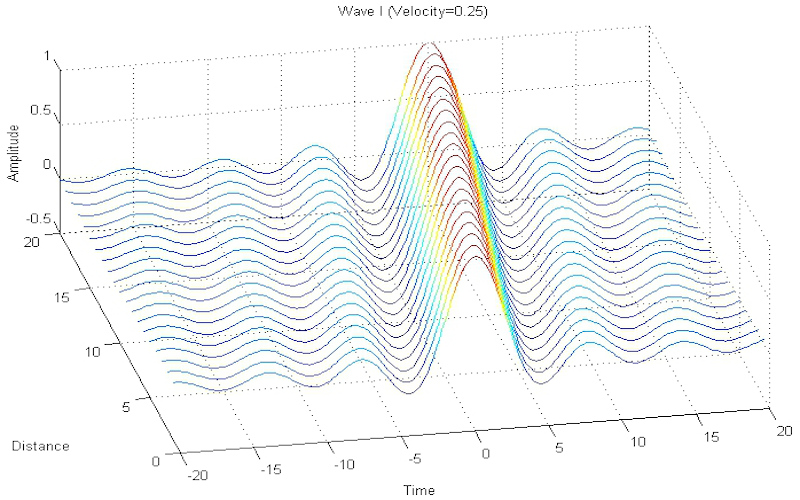
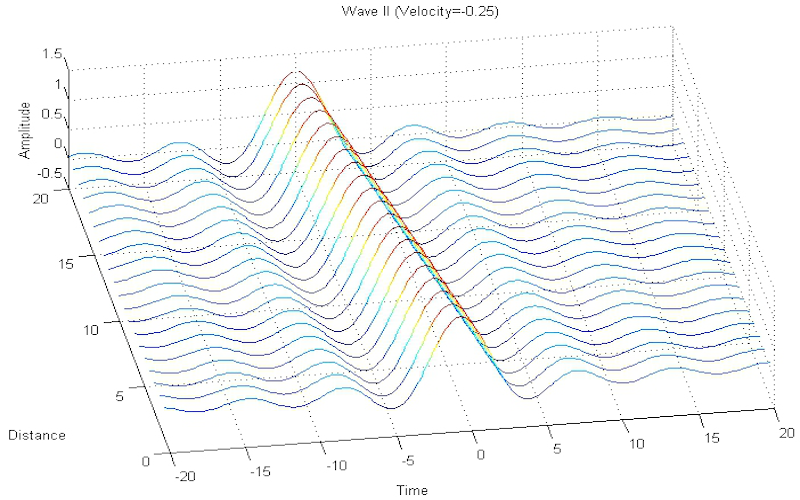
Download "TheWaveEquation"
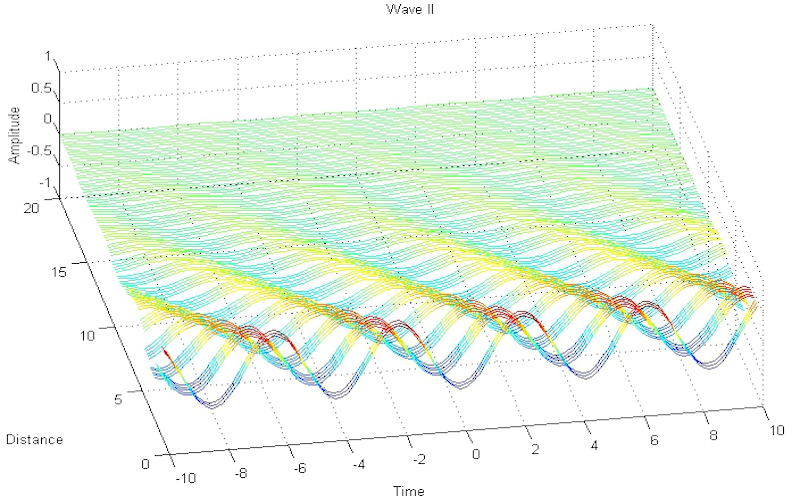
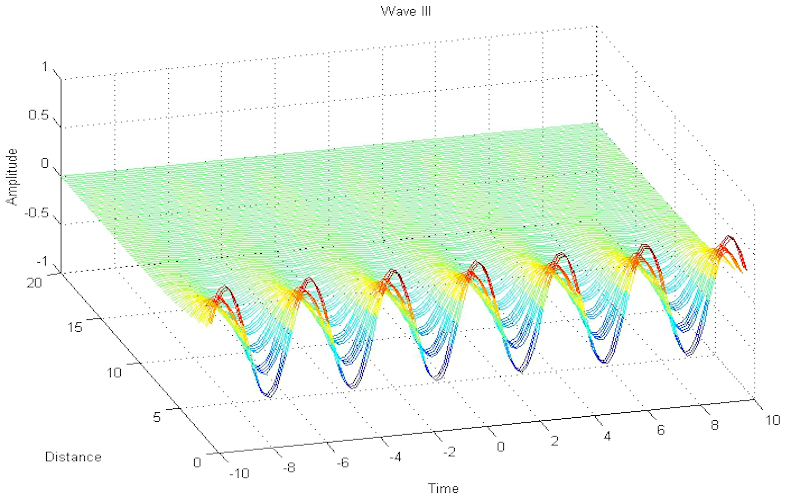
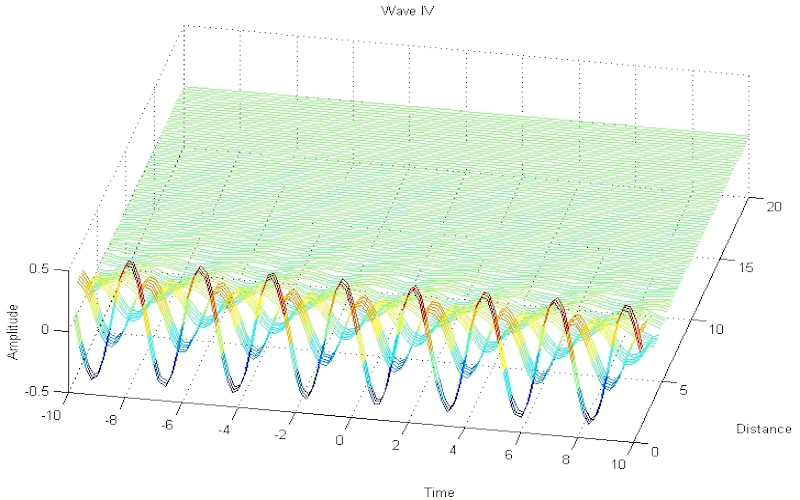
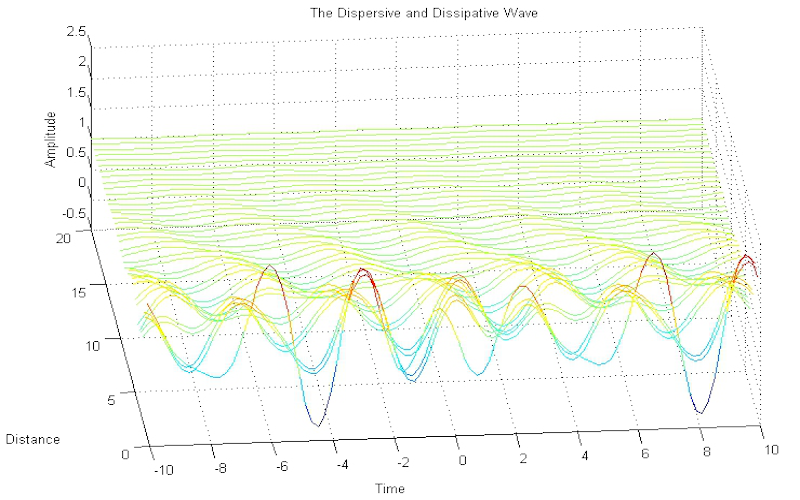
Download "WaveDispersionAndDissipation"
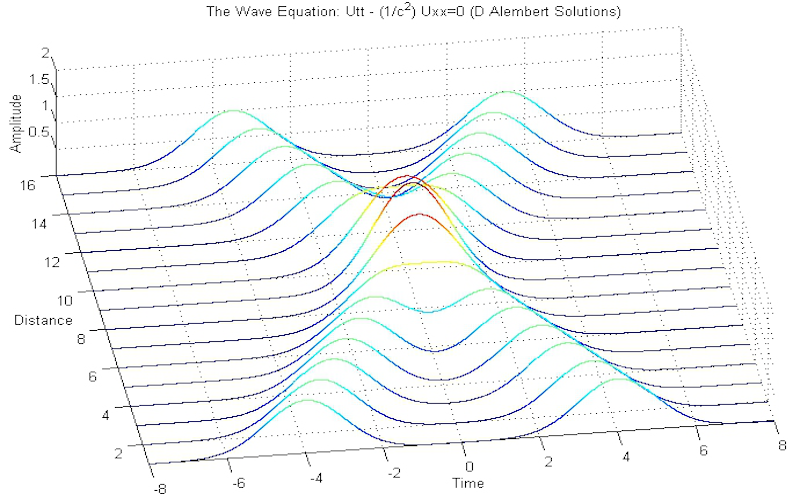
Download "WaveEquationDAlembertSolutions"
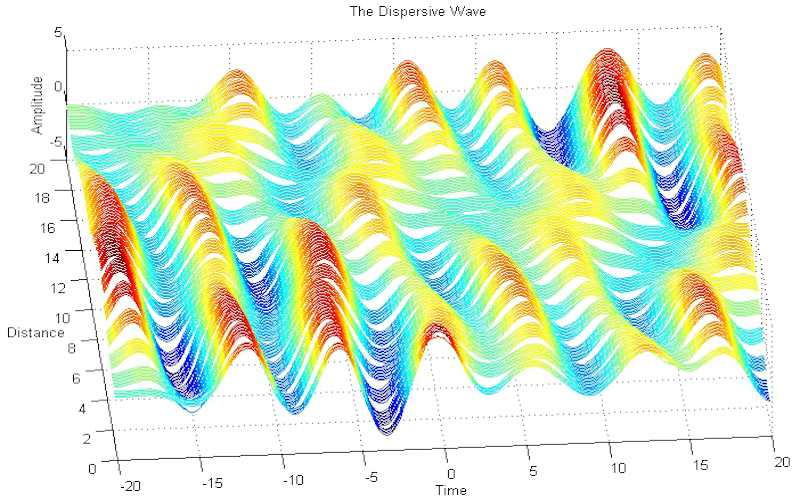
Download "WaveWithDispersion"
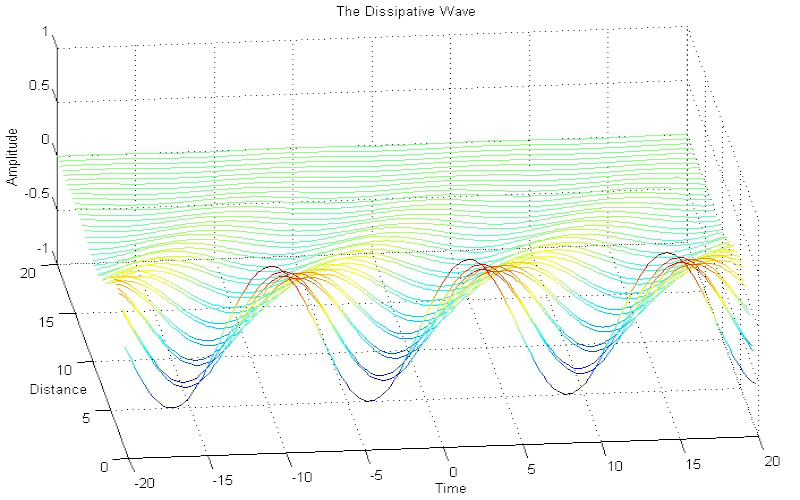
Download "WaveWithDissipation"